Understanding Gallstones: When Abdominal Pain Signals a Problem
Gallstones represent one of the most common digestive system conditions affecting millions of people worldwide, with abdominal ultrasound serving as the definitive diagnostic tool for their detection. Recent meta-analysis research demonstrates that ultrasound achieves remarkable accuracy rates of 94% sensitivity and 93% specificity specifically for gallstone detection, making it the unquestioned gold standard for this condition [1].
The formation of gallstones occurs when the delicate chemical balance of bile within the gallbladder becomes disrupted. Your gallbladder, a small pear-shaped organ positioned beneath the liver, stores bile produced by the liver to aid in fat digestion. When this bile contains excessive cholesterol, bilirubin, or when the gallbladder fails to empty properly, crystalline deposits form that can range from tiny sand-like particles to stones as large as golf balls [2].
Understanding the underlying mechanisms of gallstone formation provides insight into why ultrasound proves so effective for diagnosis. Cholesterol gallstones, which account for approximately 75% of all cases, develop when the liver secretes more cholesterol than the bile can dissolve [2]. The excess cholesterol crystallizes and gradually accumulates into stones. Pigment gallstones, appearing dark brown or black, form when bile contains excessive bilirubin, often resulting from liver cirrhosis, biliary tract infections, or certain blood disorders [2].
The location of gallstones significantly impacts both symptoms and diagnostic approaches. While most stones remain within the gallbladder itself, some migrate into the bile ducts, a condition known as choledocholithiasis, or even into the liver's intrahepatic ducts. This variation in location explains why comprehensive abdominal ultrasound examinations evaluate not only the gallbladder but also the surrounding biliary tree and related organs.
Recognizing Gallstone Symptoms: When to Seek Ultrasound Diagnosis
Many individuals with gallstones experience no symptoms whatsoever, a condition termed "silent gallstones." However, when stones obstruct bile flow or irritate the gallbladder walls, they trigger a characteristic pattern of symptoms that warrant immediate ultrasound evaluation.
The hallmark symptom of gallstone disease is biliary colic, characterized by sudden, intense pain in the upper right portion of the abdomen that may radiate to the center of the abdomen just below the breastbone [2]. This pain often extends between the shoulder blades and into the right shoulder, creating a distinctive pattern that experienced healthcare providers readily recognize. The pain typically intensifies rapidly, reaching peak intensity within minutes, and may persist for several minutes to several hours before gradually subsiding.
Common Gallstone Symptoms
| Symptom Type | Description | Duration | Triggers |
| Biliary Colic | Sudden, intense upper right abdominal pain | Minutes to hours | Fatty meals, large meals |
| Referred Pain | Pain between shoulder blades, right shoulder | Concurrent with abdominal pain | Same as biliary colic |
| Nausea/Vomiting | Digestive upset, particularly after eating | Variable | Fatty or greasy foods |
| Jaundice | Yellowing of skin and eyes | Persistent until treated | Bile duct obstruction |
| Fever/Chills | Signs of infection or inflammation | Persistent | Acute cholecystitis |
The Science Behind Ultrasound Accuracy for Gallstone Detection
Ultrasound Diagnostic Performance Comparison
| Condition | Sensitivity | Specificity | Clinical Significance |
| Gallstones (Cholelithiasis) | 94% | 93% | Excellent accuracy for stone detection |
| Acute Cholecystitis | 73% | 93% | Good for inflammation detection |
| Overall Gallbladder Disease | 86% | 92% | Reliable first-line diagnostic tool |
Comprehensive Ultrasound Procedure: What Patients Can Expect.
Pre-Examination Preparation Timeline
| Time Before Exam | Requirements | Rationale |
| 24 Hours | Light, low-fat dinner | Reduces gallbladder stimulation |
| 12 Hours | Begin fasting period | Allows gallbladder to fill with bile |
| Day of Exam | No food or drink (except small sips of water if permitted) | Maintains gallbladder distension |
| Arrival | Comfortable clothing, remove jewelry | Facilitates examination access |
Upon arrival for the examination, patients typically change into a hospital gown and remove jewelry that might interfere with the procedure. Personal belongings are secured in lockers near the examination room. The examination room itself is designed for patient comfort, with dimmed lighting to optimize image viewing and comfortable positioning equipment.
During the procedure, patients lie on their back on a padded examination table. The sonographer applies a clear, water-based gel to the abdomen, which serves as a coupling agent between the ultrasound transducer and the skin. This gel eliminates air pockets that would otherwise interfere with sound wave transmission, ensuring optimal image quality throughout the examination.
The sonographer systematically examines the gallbladder and surrounding structures using a handheld transducer. This device emits high-frequency sound waves and receives the returning echoes, which are processed by sophisticated computer systems to create real-time images. The examination typically requires 20-30 minutes to complete, during which the sonographer captures multiple images from different angles and positions.
Interpreting Ultrasound Results: Understanding Your Diagnosis
Ultrasound Findings and Their Clinical Significance
| Finding | Ultrasound Appearance | Clinical Meaning | Next Steps |
| Normal Gallbladder | Thin wall (<3mm), anechoic bile | No gallbladder disease | Routine follow-up |
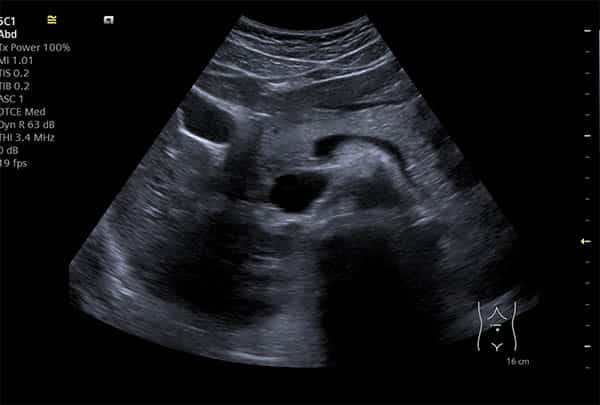
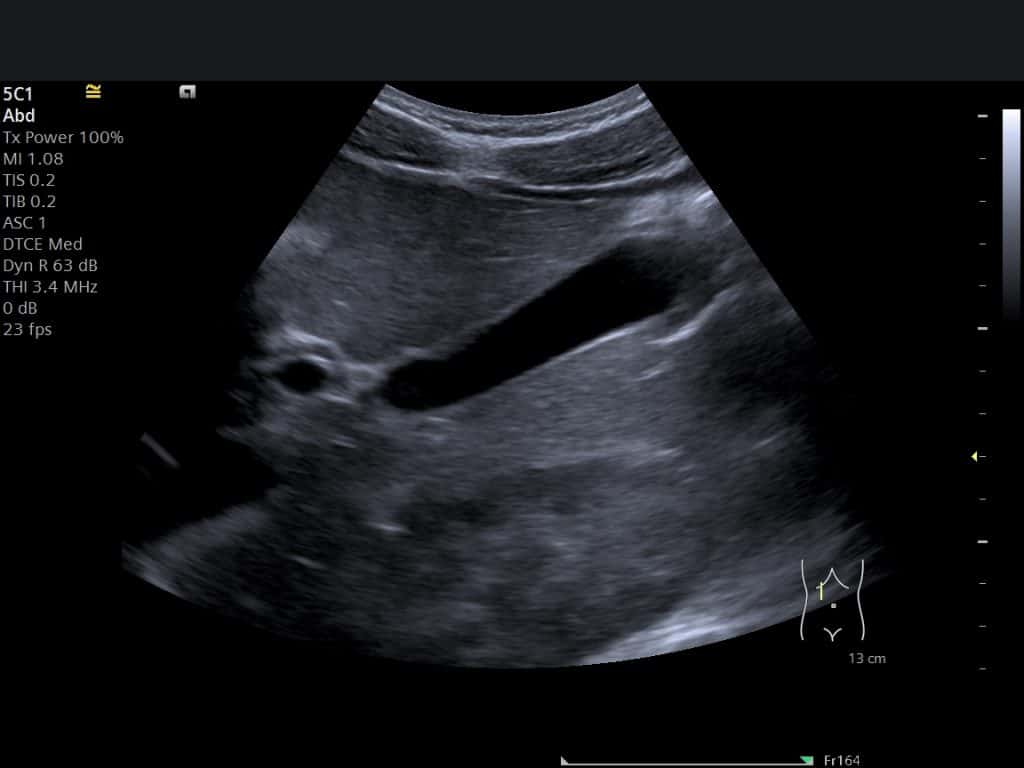
| Gallstones | Hyperechoic with acoustic shadowing | Stone presence confirmed | Symptom assessment, treatment planning |
| Wall Thickening | Wall >3mm thick | Possible cholecystitis | Clinical correlation, possible treatment |
| Bile Duct Dilation | Dilated common bile duct | Possible obstruction | Urgent evaluation needed |
| Pericholecystic Fluid | Fluid around gallbladder | Inflammation/infection | Immediate medical attention |
Ultrasound vs. Other Diagnostic Methods: Making the Right Choice
Diagnostic Imaging Comparison for Gallbladder Disease
| Imaging Method | Sensitivity for Stones | Sensitivity for Cholecystitis | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Ultrasound | 94% | 73% | No radiation, immediate, cost-effective | Operator dependent |
| CT Scan | Variable | 81-85% | Comprehensive, detects complications | Radiation exposure, higher cost |
| MRI/MRCP | ~90% | ~90% | Excellent soft tissue contrast | Expensive, limited availability |
| HIDA Scan | N/A | ~95% | Functional assessment | Time-consuming, radiation |
Risk Factors and Prevention: Understanding Your Gallstone Risk
Major Risk Factors for Gallstone Development
| Risk Category | Specific Factors | Relative Risk | Modifiable |
| Demographic | Female gender, Age >40, Native American/Hispanic ethnicity | High | No |
| Medical | Diabetes, Liver disease, Blood disorders | Moderate-High | Partially |
| Lifestyle | Obesity, Sedentary lifestyle, Rapid weight loss | High | Yes |
| Dietary | High-fat diet, Low-fiber diet, Skipping meals | Moderate | Yes |
| Hormonal | Pregnancy, Estrogen therapy, Oral contraceptives | Moderate | Partially |
Treatment Options: From Conservative Management to Surgical Intervention
Treatment Decision Matrix
| Clinical Scenario | Recommended Approach | Rationale | Expected Outcome |
| Asymptomatic Stones | Watchful waiting | Low symptom development risk (10-30%) | Monitor for symptom development |
| Symptomatic Stones | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy | Definitive treatment, prevents recurrence | Excellent long-term results |
| Acute Cholecystitis | Urgent cholecystectomy | Prevents complications | High success rate |
| High Surgical Risk | Medical management | Avoid operative risks | Symptom control |
| Bile Duct Stones | ERCP + cholecystectomy | Address stones and source | Comprehensive treatment |
Private Ultrasound Services: Advantages and Considerations
Private vs. NHS Ultrasound Services Comparison
| Aspect | Private Services | NHS Services |
| Availability | Same-day/next-day appointments | Weeks to months waiting |
| Scheduling | Flexible hours, weekends | Limited scheduling options |
| Examination Time | Extended consultation time | Standard protocol timing |
| Equipment | Latest technology | Standard equipment |
| Reporting | Immediate specialist review | Standard reporting timeline |
| Cost | Out-of-pocket expense | Free at point of care |
| Comprehensive Scope | Full upper abdominal scan | Focused gallbladder assessment |
Frequently Asked Questions About Gallstone Ultrasound
Taking Control of Your Gallbladder Health
References
Content Information
We review all clinical content annually to ensure accuracy. If you notice any outdated information, please contact us at info@iuslondon.co.uk.
About the Author:

Yianni is a highly experienced sonographer with over 21 years in diagnostic imaging. He holds a Postgraduate Certificate in Medical Ultrasound from London South Bank University and is registered with the Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC: RA38415). Currently working at Barts Health NHS Trust, Yianni specialises in abdominal, gynaecological, and obstetric ultrasound. He is a member of the British Medical Ultrasound Society (BMUS), Society of Radiographers (SoR) and regularly contributes to sonographer and junior radiologists training programs.