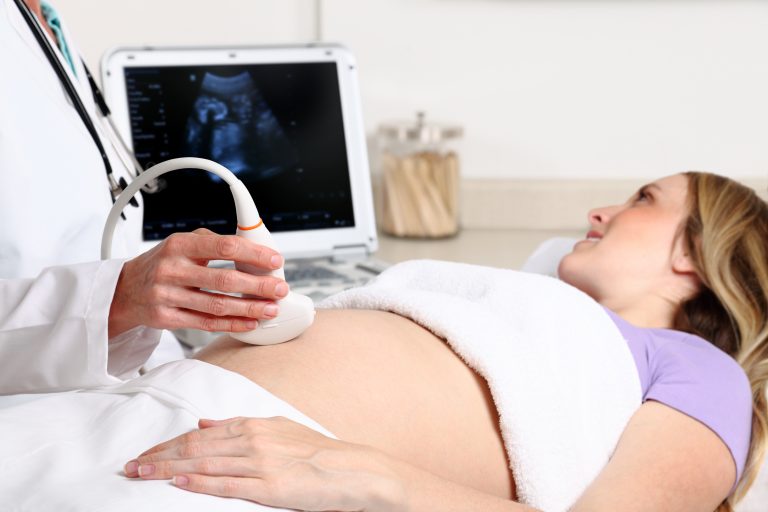
Medical imaging offers patients and healthcare providers essential insights into health and disease, and at the heart of these services stands the sonographer. In an ultrasound exam, the sonographer’s role is crucial, combining medical knowledge with technical skills to produce images that inform diagnosis, treatment, and management. Whether it’s examining abdominal organs, assessing blood flow in veins, or monitoring pregnancy, the sonographer’s expertise directly impacts patient care.
What is a Sonographer?
A sonographer, also known as an ultrasound technologist, is a healthcare professional trained to perform diagnostic medical sonography, commonly called ultrasound. Using high-frequency sound waves, sonographers produce real-time images of the body’s internal structures. Sonography is a non-invasive, radiation-free imaging technique, which makes it highly safe and suitable for various medical applications.
The sonographer’s scope of work extends beyond simply operating ultrasound machines. They must understand human anatomy, pathology, and physics to recognize normal and abnormal findings in different body areas. While sonographers do not diagnose conditions (this responsibility lies with radiologists and other physicians), their skill in capturing high-quality images is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
Training and Qualifications of a Sonographer
Becoming a qualified sonographer requires a strong foundation in medical science and specialized training in ultrasound imaging. Sonography programs vary across regions, with entry pathways typically including an associate’s degree, bachelor’s degree, or postgraduate diploma in diagnostic medical sonography.
The program covers anatomy, physiology, patient care, physics, and ultrasound imaging techniques, preparing students to handle various clinical scenarios. After completing the required education, prospective sonographers undertake certification exams. In the UK, for instance, sonographers often obtain credentials from recognized bodies like the Society and College of Radiographers or the Consortium for the Accreditation of Sonographic Education.
Continuous professional development (CPD) is fundamental to maintaining and enhancing skills. This includes attending workshops, conferences, and courses to stay updated on advancements in ultrasound technology and techniques. Specialization options are also available, allowing sonographers to focus on areas like vascular ultrasound, musculoskeletal ultrasound, and obstetric sonography.
Skills and Expertise of an Experienced Sonographer
Sonography is both an art and a science. Sonographers use their technical expertise to operate complex ultrasound equipment, but experience also plays a critical role in producing accurate and detailed images. Experienced sonographers possess a unique blend of technical, interpersonal, and analytical skills that enable them to provide top-notch care.
-
Technical Proficiency: Experienced sonographers have an in-depth understanding of ultrasound equipment. They know how to adjust machine settings, manipulate transducers, and position patients to capture the most informative images. This level of proficiency leads to clearer, more accurate scans that aid in diagnosis.
-
Analytical Skills: A trained eye and an analytical mind are vital in distinguishing normal from abnormal findings. Recognizing subtle changes in tissue structure or blood flow can help identify conditions early. Seasoned sonographers develop these skills over years of clinical practice, making them adept at capturing the right images in complex cases.
-
Interpersonal Skills: Sonographers often work closely with patients who may feel anxious or uncomfortable. An experienced sonographer can put patients at ease, explaining procedures clearly and helping them relax. A calm, empathetic approach not only improves patient comfort but also aids in obtaining high-quality images.
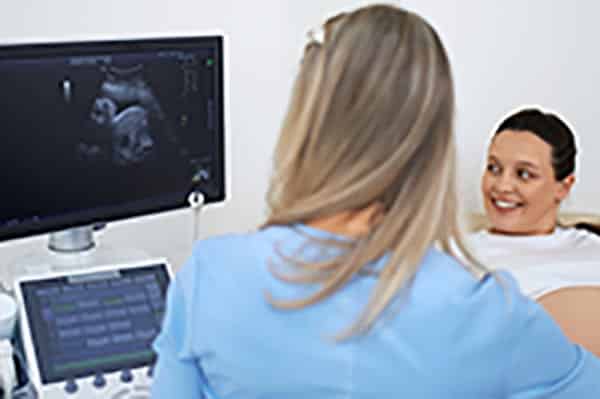
The Role of a Sonographer in Patient Care
Sonographers play a crucial role in the diagnostic process, capturing real-time images that inform decisions across specialties, including obstetrics, cardiology, and gastroenterology. An ultrasound scan involves much more than simply generating images. Each scan requires a tailored approach to meet specific diagnostic objectives, making the sonographer’s role essential in guiding patient care.
Effective communication is at the heart of the sonographer’s role. Explaining what to expect during the exam, answering questions, and addressing concerns are all part of the job. This interaction can significantly reduce patient anxiety, especially in cases where ultrasound exams involve sensitive areas or conditions. Experienced sonographers strike a balance between professionalism and warmth, ensuring patients feel respected and informed throughout the procedure.
What to Expect During Your Ultrasound Examination
For those unfamiliar with ultrasound, understanding what happens during the exam can be helpful. The process typically starts with a referral from a physician, who will specify the area or condition to be examined.
During the appointment, the sonographer may ask you to change into a gown and lie on an examination table. A clear, water-based gel will be applied to your skin over the area being scanned. This gel helps transmit the sound waves more effectively and improves image quality. Using a handheld device called a transducer, the sonographer gently moves it over the area, adjusting angles and pressure to capture the best possible images.
Throughout the exam, the sonographer may ask you to change positions, hold your breath briefly, or follow other instructions to obtain optimal images. These adjustments help ensure the sonographer captures images from multiple perspectives, aiding the radiologist or physician in making an informed diagnosis.
After the scan, the images are reviewed, often by a radiologist, who interprets them and provides a report to the referring doctor. The sonographer, however, is instrumental in producing accurate images that support the interpretation process.
Why Expertise Matters: Choosing a Qualified Sonographer
The experience and qualifications of the sonographer performing your scan can directly affect the quality and accuracy of the results. With advancements in ultrasound technology, having a skilled sonographer is more important than ever. Knowledgeable sonographers can adapt to various clinical situations, ensuring each scan meets high standards and provides reliable insights.
Choosing a sonographer with experience in the specific area being examined, such as vascular or obstetric ultrasound, can make a significant difference in diagnostic accuracy. A study in the Journal of Clinical Ultrasound found that experience in the field is associated with better outcomes in terms of image quality and diagnostic reliability. Additionally, skilled sonographers are often more adept at handling complex cases and tailoring their approach to individual patients, a quality that benefits both patients and healthcare providers.
If you’re arranging a scan, you might want to inquire about the sonographer’s background, certifications, and areas of specialization. Opting for a reputable ultrasound service can ensure that you receive a high-quality scan from a professional who is fully qualified and experienced.